3 Types of Access Rights in Teradata
There are 3 types of access rights in Teradata. How these access rights will obtain? Let us see full details.
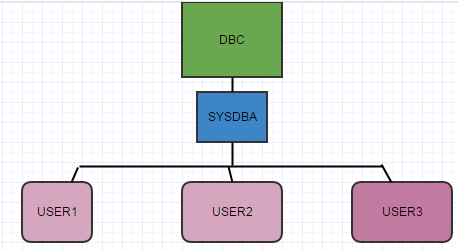
DBC is default user, under it SYSDBA will come, and then other users will come. DBC is super user, it has full powers, and credentials should be Confidential.
Implicit rights : Belong to the owners of objects. Owners don't require rows in the DBC.AccessRights table to grant privileges on owned objects. Ownership rights can't be revoked. A parent or owner has the implied right to GRANT privileges over their children. DBC and SysDBA hold implicit roles on all the other databases above.
Automatic rights: Happen whenever a CREATE statement is submitted, and new rows are automatically added to the DBC.AccessRights table. When the databases above were created, they automatically received all but four access rights on themselves. Automatic rights are removed with REVOKE or DROP statements.
Explicit rights : are completely controlled by when a user explicitly and literally submits a GRANT or REVOKE statement. The GRANT statement adds new rows to the DBC.AccessRights table, and the rights are granted. The REVOKE removes them.
DBC is default user, under it SYSDBA will come, and then other users will come. DBC is super user, it has full powers, and credentials should be Confidential.
Implicit rights : Belong to the owners of objects. Owners don't require rows in the DBC.AccessRights table to grant privileges on owned objects. Ownership rights can't be revoked. A parent or owner has the implied right to GRANT privileges over their children. DBC and SysDBA hold implicit roles on all the other databases above.
Automatic rights: Happen whenever a CREATE statement is submitted, and new rows are automatically added to the DBC.AccessRights table. When the databases above were created, they automatically received all but four access rights on themselves. Automatic rights are removed with REVOKE or DROP statements.
Explicit rights : are completely controlled by when a user explicitly and literally submits a GRANT or REVOKE statement. The GRANT statement adds new rows to the DBC.AccessRights table, and the rights are granted. The REVOKE removes them.



Comments
Post a Comment